
Here we discuss the various examples to understand the numpy interp function and its uses.Datashader renders data into regularly sampled arrays, a process known as rasterization, and then optionally converts that array into a viewable image (with one pixel per element in that array). Similarly, we can use the interp function to find unknown values for various functions.
#Interpolate numpy raster x y z how to
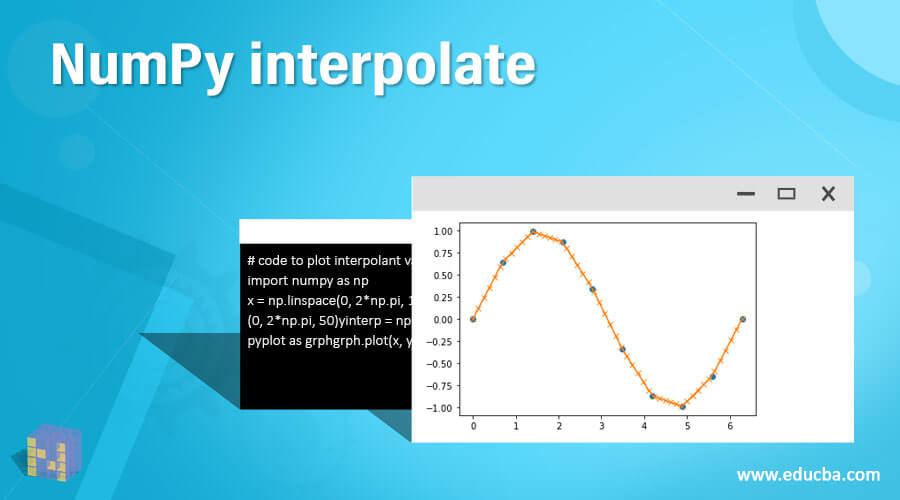
We have also discussed how to find interpolant values for the sine function as well. This article discussed the Numpy Interp function in detail using various examples to get a clear understanding of the numpy interp function and its uses. In the last step, we are plotting the graph and displaying the output. Then we are importing the matplotlib.pyplot library to plot the curve. Then we are finding the interpolant values using the interp function. In the above example, we are declaring x and y coordinates as a sine function. X = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 10)y = np.sin(x)x_values = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 50)yinterp = np.interp(x_values, x, y)import matplotlib.pyplot as ot(x, y, 'o')ot(x_values, yinterp, '-x')grph.show()
#Interpolate numpy raster x y z code
Let’s try to find the interpolant values for the sine function.Ĭode: # code to plot interpolant values for the sine function. Finally, in the last step, we have printed the interpolated values. In the next step, interpolation is done using the interp function. In the next step, we have printed the two arrays. Then we have assigned five values to the one-dimensional array x, for which we need to find the y coordinates. Here in the above example, we have declared two one-dimensional arrays, xp and fp, which contains the x coordinates and y coordinates of discrete data points. Print ("The interpolated values are ", interpolated_value) This example will discuss how we can use the decimal argument to understand the interpolation concept better.Ĭode: # simple program in python to explain interpolation In the second condition, we check the y coordinates, and the result is false. In the first condition, we check the x coordinates, and the result is true. In the above example, you can see that the x coordinates are continuously increasing, and the y coordinates are continuously decreasing. To check whether the sequence is increasing continuously, follow the step shown below.Ĭode: # program to check whether x coordinates are strictly increasing. If the x coordinate values are not increasing, then the results of interpolated values are meaningless. The x coordinates must be continuously increasing. The interpolated value returned is 2.5 for the value x = 5.
In the last step, we have printed the interpolated value. Then we have assigned a value of 5 to the one-dimensional array x, for which we need to find the y coordinate. Print ("The interpolated value for x = 5 is ", interpolated_value) Interpolated_value = np.interp(x, xp, fp) Let us discuss a basic example for understanding how the numpy interpolate function works.Ĭode: # simple program in python to explain numpy.interp() function Given below are the examples of NumPy interpolate: Example #1

The data type will be either float or complex depending on the fp data points or n-dimensional array.


xp: It refers to the one-dimensional sequence of float data type, which contains the x coordinates of the data points.It contains the x coordinates of the interpolated data points. x: it is a one-dimensional array for which we need to do interpolation.It will return the one-dimensional piecewise linear interpolant values to the function given with distinct data points xp and fp, which is evaluated at x. The above-mentioned syntax is for one-dimensional linear interpolation. Numpy.interp(x, xp, fp, left=none, right=none, period=none)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
